We will study so I can to by .
You may have heard people talking about using a program, an application, or an app. But what exactly does that mean? Simply put, an app is a type of software that allows you to perform specific tasks. Applications for desktop or laptop computers are sometimes called desktop applications, while those for mobile devices are called mobile apps.
When you open an application, it runs inside the operating system until you close it. Most of the time, you will have more than one application open at the same time, which is known as multi-tasking.
App is a common term for an application, especially for simple applications that can be downloaded inexpensively or even for free. Many apps are also available for mobile devices and even some TVs.
Watch the video below to learn more about applications.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still view it here.
There are countless desktop applications, and they fall into several categories. Some are more full featured (like Microsoft Word), while others may only do one or two things (like a clock or calendar app). Below are just a few types of applications you might use.



Desktop and laptop computers aren’t the only devices that can run applications. You can also download apps for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Here are a few examples of mobile apps.

Every computer and mobile device will come with some applications already built in, such as a web browser and media player. However, you can also purchase and install new apps to add more functionality. You can review our lessons on Installing Software on Your Windows PC, Installing Software on Your Mac, and Free Software to learn more.

While exploring the Internet, you’ve probably encountered the terms downloading and uploading. Downloading means receiving data or a file from the Internet on your computer. Uploading means sending data or a file from your computer to somewhere on the Internet.
These terms describe activities you may have already learned how to do. If you’ve ever opened an example document in one of our tutorials, you’ve downloaded that file. If you’ve ever shared a photo you took on Facebook or another social media site, you’ve uploaded that photo.
Usually, when you download a file you will start the download by clicking a link to that file. Many of our tutorials contain links to files, like this:
Download our practice document.
If you click the link, your browser should prompt you to select one of two methods for downloading the file.
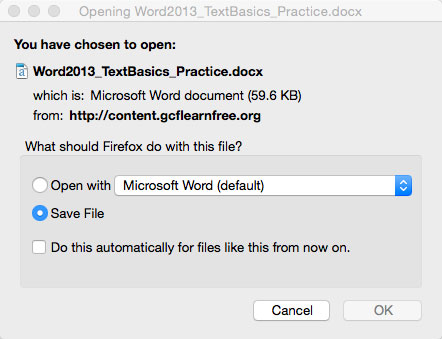
Either way, once you click OK, the download begins. Your browser will indicate the progress and time remaining on the download.

Once the download is complete, either the file will be saved to your computer or it will open in the program you selected. If you have trouble finding the file after you’ve downloaded it, check out our Finding Your Downloads lesson.
Some browsers don’t always start this download process when you click the link to a file. In these cases, you can right-click the link, then click Save Link As, then select a location to download the file.
If a site allows uploads, it will have an upload utility to help perform the file transfer. Each site handles this process differently, but we’ll give some common examples. Usually, the site will have help pages to walk you through the upload process.
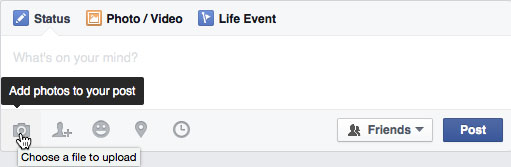
Many sites have an upload button that opens a dialog box. For example, Facebook has a camera icon that begins the upload process.
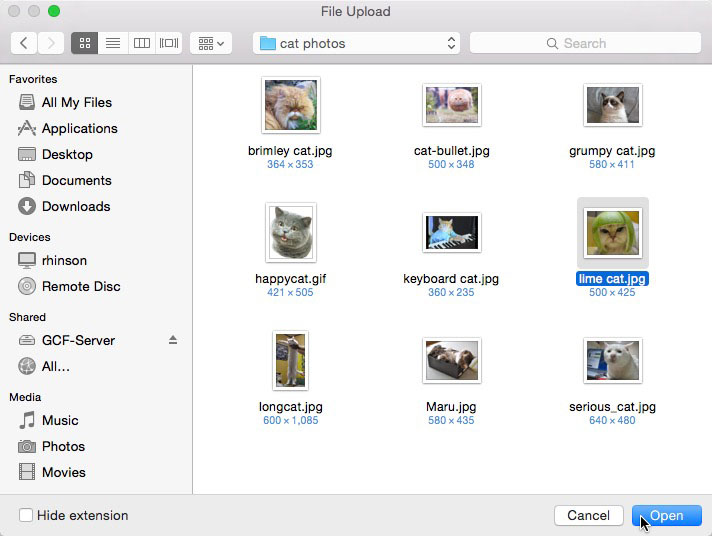
A dialog box will appear, prompting you to select a file. Browse to the location where your file is stored, select it, then click the Open button. Afterward, a progress bar tracking the upload process will appear on the page.
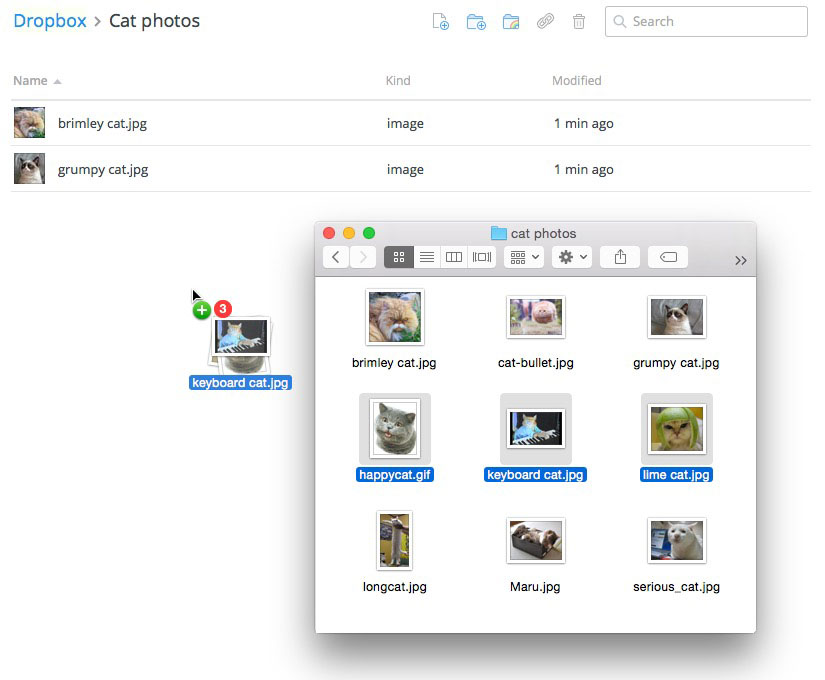
Some sites support a drag-and-drop interface. For example, when logged in to Dropbox you can drag the files from a folder on your computer and drop them into the browser window.
Many other upload utilities have similar features. A more detailed example of uploading a file is available in our Google Drive tutorial.