Key Concepts:
Vocabulary: communicable disease, epidemic
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
What Are STDs?
Main Idea: Anyone who has sexual contact with another person risks contracting a sexually transmitted disease.
Sexually transmitted diseases {STDs) are infections spread from person to person through sexual contact. Also known as sexually transmitted infections {STls), STDs are communicable diseases that can be easily transmitted from one person to another. For an infection to occur, a person must engage in sexual activity that involves direct genital contact or the exchange of semen or other body fluids with someone infected with an STD. Some STDs are caused by a bacterial infection and can be cured with medication. Other STDs are caused by viruses and are incurable. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to controlling or curing an STD.
However, several of the most common STDs are often asymptomatic, meaning that individuals show no symptoms, or the symptoms are mild and disappear after the onset of the infection. This lack of symptoms makes STDs particularly dangerous. A person may not realize that he or she is infected. Therefore, he or she may not seek treatment. An individual with an undiagnosed STD may unknowingly pass the infection on to future sexual partners.
Any person who has sexual contact with another person risks contracting an STD. The risk of contracting an STD also increases as the number of sexual partners increases. It is estimated that approximately 9 million young people between the ages of 15 and 24 will become infected with an
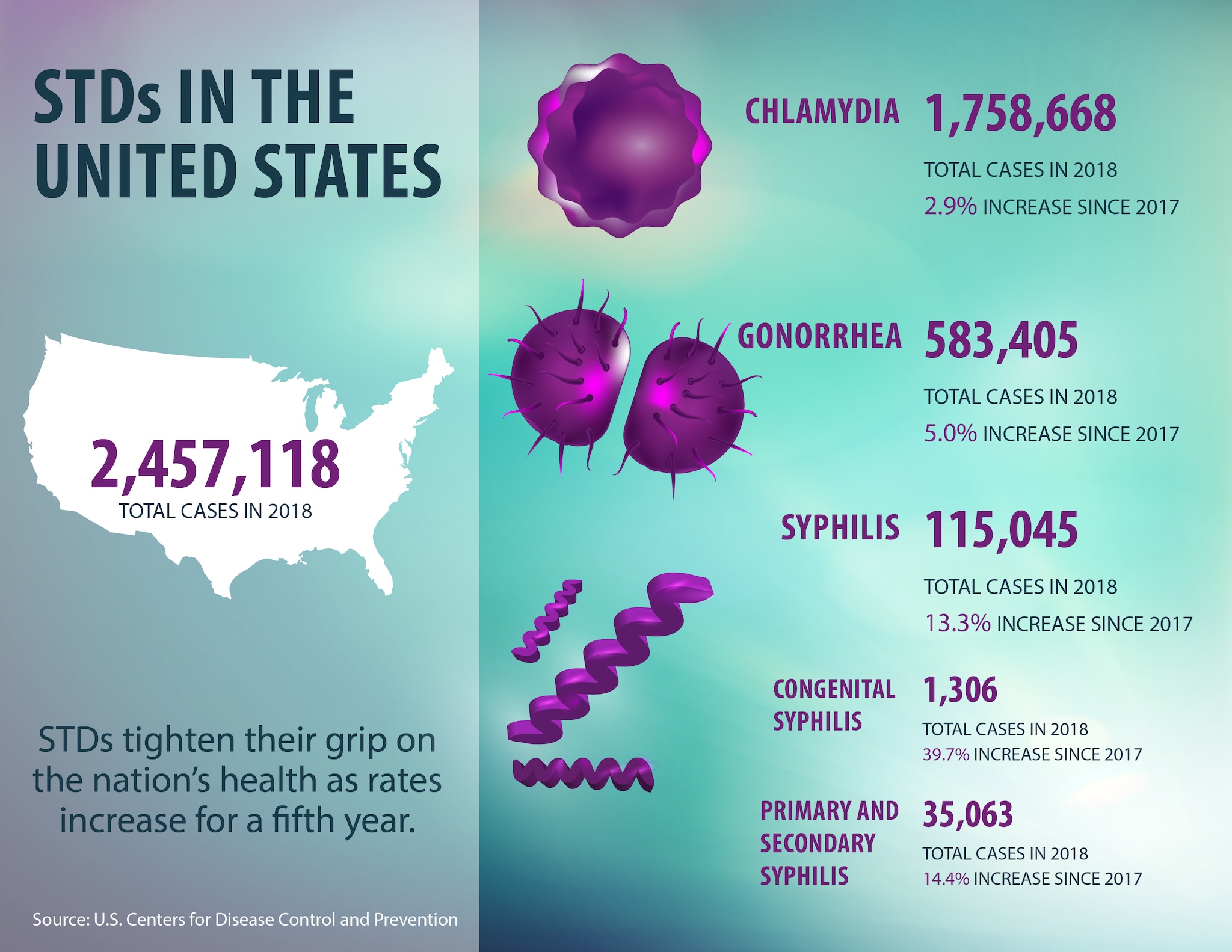
STD each year. As Figure 24.1 shows, many of these cases will not be diagnosed, treated, or reported, creating a serious health crisis. Females are more likely to suffer complications from STDs, and the effects are more serious in females than in males. Both the physical and psychological effects on people infected with STDs are significant, and so the consequences for health care in the United States are serious as well. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that direct medical costs connected to STDs are now at more than $15.3 billion a year.
Common STDs
Main Idea: There are approximately 25 different STDs, six of which are considered the most common.
Of the approximately 25 STDs worldwide, the following six are considered the most common: genital HPV infections chlamydia, genital herpes, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, and syphilis. Figure 24.3 shows the symptoms and possible long- term effects of these STDs.
Genital HPV Infections
Genital HPV infections are caused by human papillo- mavirus (HPV), a group of more than 100 kinds of viruses. More than 30 ofthese viruses are transmitted through sexual contact. Close to 6 million people in the United States are infected with HPV each year.
HPV infections can cause genital warts, which appear as bumps or growths near or on the genitals. Most genital HPV infections do not have symptoms and will disappear without medical treatment. However, some HPV infections, if not diagnosed and treated, may cause abnormal Pap tests or, more seriously, may result in certain types of cervical cancer. A vaccine treatment is now available for protection against HPV. It is not a cure, but is recommended to reduce the number of cases of cervical cancer.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs of both males and females. About 2.8 million Americans contract chlamydia each year, with the disease affecting young females three times more often than males. However, less than half of all cases are reported. As with genital HPV, chlamydia often produces no symptoms. Thus, sexually active teens may not know they are infected, do not seek testing, and go untreated. Chlamydia is still the most common STD among teens.
If left untreated, chlamydia can cause serious complica- tions. Females can develop pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and suffer chronic pelvic pain or infertility. Untreated chla- mydia can also lead to infertility in males. Pregnant females with chlamydia can deliver prematurely, and the infants born to infected mothers may develop eye disease or pneumonia, as well as fatal complications. Females with chlamydia are up to five times more likely to become infected with HIV if exposed to the virus.
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes simples 1 usually causes cold sores in or near the mouth. Herpes simples 2 typically causes genital sores. Both types, however, can infect the mouth and genitals.
Many people infected with genital herpes are asymptomatic and are not aware they have the infection. If symptoms do occur, the first outbreak will usually appear as blisters on the genitals or rectum within two weeks of the virus being transmitted. The blisters break, leaving sores that can take several weeks to heal. Usually the first sores are followed by shorter, less sever outbreaks that can occur on and off for years. Antiviral treatments can lessen the frequency of outbreaks, but there is not cure for genital herpes.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a bacterial STD that usually affects mucous membranes. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease in the United States. The CDC estimates that more than 700,000 Americans are infected with gonor-rhea each year, but only half of these are reported.
Many males with gonorrhea are asymptomatic, and infected females show only mild symptoms. Left untreated gonorrhea can cause severe health problems, such as infertil~ ity. The bacteria can also spread to the bloodstream and cause permanent damage to the body’s joints. Females can pass the infection to their babies during childbirth. These babies may contract eye infections that cause blindness.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is caused by a microscopic protozoan that results in infections of the vagina, urethra, and bladder. About 7.4 million new cases of trichomoniasis occur every year in the United States.
Although the disease may not produce symptoms, some males have a temporary irritation inside the penis, mild dis- charge, or slight burning during and after urination or ejaculation. Many infected females often experience vaginitis, an inflammation of the vagina characterized by discharge, odor, irritation, and itching. Females with trichomoniasis are also more likely to contract HIV if they are exposed to it. Babies born to females with trichomoniasis are often premature and have low birth weights.
Syphilis
Syphilis, an infection caused by a small bacterium called a spirochete, attacks many parts of the body. People with syphilis develop sores in the genital area lasting a couple ofweeks. The disease is passed from one person to another by direct contact with the sores during sexual activity.
Syphilis progresses through three stages. During the pri- mary stage, a sore appears on the external genitals or the vagina. At this stage, the disease can be easily treated. If the infection goes untreated, the sore heals, but the infection remains. In the second stage, the infection produces a skin rash. As in the first stage, the untreated rash will disappear, but the infection remains and progresses to the third stage. During this stage, syphilis can damage internal organs, cause brain dementia, and may cause death.
The STD Epidemic
Main Idea: Accurate health information and responsible behavior will help fight the STD epidemic.
The United States currently faces an STD epidemic. The CDC estimates that each year, 19 million people are infected with an STD. Almost half are under the age of 24. Many STD cases go undiagnosed and untreated because of embarrassment or fear. Some people are too embarrassed or afraid to seek medical help lack of symptoms. Many people infected with STDs are asymptomatic, and are unaware they have a disease. If STD symptoms disappear without treatment, the infected person may mistakenly believe the disease has been cured. People may not have all the facts and may receive wrong information from friends.
State laws require health care providers to report certain but not all STDs. People who have contracted HPV infections or genital herpes are not required to report their infections or inform any partners of their condition. Infected individuals may unknowingly transmit the disease to others.